Abstract
Background: Due to better understand of biology of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), in 2017 a new era of targeted therapy has began. Before that, since 1973 younger and fit patients were offered the 3+7 regimen (based on anthracyclines and cytarabine) followed by high-dose cytarabine and, generally allogeneic stem cell transplantation in first complete remission (alloHSCT). In 2008 azacytidine, a hypomethylating (HM) agent was approved in Europe for AML patients, who were not candidate for intensive therapy and alloHSCT. In 2010 the European LeukemiaNet (ELN), based on cytogenetic and molecular genetic characteristics, proposed a risk score classification to facilitate decisions, including indications for alloHSCT. In addition to these advances, improved supportive therapies over the last 25 years are thought to have lowered therapy associated mortality.
Aims: We aimed to analyse changes in outcome of AML patients treated between 1997-2016 prior to the approval of novel drugs, in order to better understand important factors contributing to patient outcome that might also contribute to the efficacy novel treatment approaches.
Methods: Quality controlled, Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) Common Data Model (CDM) harmonized data of the HARMONY alliance database coming from 100 organisations in 18 European countries were used for this study. Out of all AML records, 5359 patients diagnosed and treated with intensive regimens between 1997-2016 were identified. Patients treated with intensive regimens were identified regardless from age by the type of chemotherapy (n=4287) or by the age ≤70 (n=1072) if there was no information concerning the therapy. Patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia and those treated with targeted therapy were excluded from the analysis. Patients were categorized into 4 calendar periods: 1997-2001 (gr1), 2002-2006 (gr2), 2007-2011 (gr3) and 2012-2016 (gr4). The main outcome parameters analyzed were patient characteristics, overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS). OS and RFS were determined using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
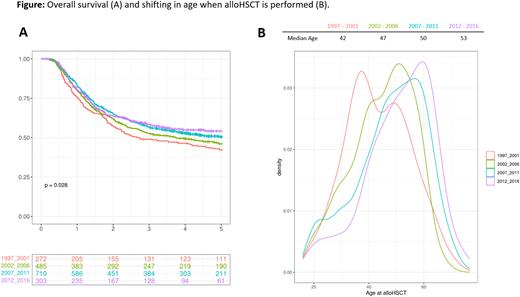
Results: 5359 AML patients were included into the analysis: 1127 in gr1, 1294 in gr2, 1821 in gr3 and 1117 in gr4. The median follow-up of all patients was of 1.9 [0-17.6] while of those who survived of 5.8 [0-17.6] years. 46.6% of patients were female. The median age of all patients was 53 years (18-85). There were 3745 patients <60, 1229 between 60-69 and 385 ≥70 years old. There were no differences in ELN risk between groups. Intensive regimens in ≥70 years AML, were less frequent through calendar period: 12% in gr1 vs 6% in gr2 vs 6% in gr3 vs 7% in gr4. AlloHSCT was performed in first remission in 1770 (33%) patients and according to calendar period: 24.1% in gr1, 37.5% in gr2, 39% in gr3, and 27% in gr4 (p<0.001). OS significantly improved over the time: 15.5 (95CI: 13.8-17.6) in gr1 vs 26.3 (23.7-31.6) in gr2 vs 39.3 (32.5-47.1) in gr3 vs 37.8 (31.6-49.2) months in gr4 (p<0.001). The OS improvement was observed for both sexes, across all 4 calendar periods, but mostly for women: 32.4 (28.8-37.8) vs 25.0 (22.5-27.7) months (p<0.001). A significant improvement in OS across the four groups was observed in AML with alloHSCT: 33 (26-56.8) vs 45.4 (34.1-65.6) vs 63 (46-not-reached) months, with group 4 not yet reaching median survival, Fig A. Interestingly, the median age to perform alloHSCT in group 1 was of 42.1 (18 - 71), while in group 2, 3 and 4 it was 46.9 (16 - 69) vs 49.9 (17 - 75) and 53 (18 - 77) years, respectively (p=0.028), Fig B.
Conclusion: Here we report the results of a large cohort of AML patients intensively treated between 1997-2016. Improvement of survival was observed for patients treated between 2007-2016 vs 1997-2007 in parallel with performing alloHSCT at more advanced age, most likely due to better supportive care and a greater proportion of reduced-intensity conditioning alloHSCT. As the majority of AML patients are diagnosed at advanced age, alloHSCT should be considered a curative treatment option. Less frequency of intensive regimens in elder AML since 2002 could be related with introduction of HM agents. Less number of alloHSCT in gr4 most likely represents a bias of our data base or could be related to better patient's selection (ELN criteria) and need to be analysed in a further study. The better improvement in OS in women could be explained by the fact that globally, including AML, women live longer than men.
Disclosures
Sobas:Celgene/BMS: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Döhner:Jazz: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kronos: Research Funding. Thiede:Kronos Bio, Inc.: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AgenDix GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company. Turki:CSL Behring: Consultancy; MSD: Speakers Bureau; Jazz Pharma: Speakers Bureau. Metzeler:Daiichi Sankyo: Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Curis: Research Funding; Astellas: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria. Haferlach:Munich Leukemia Laboratory: Current Employment, Other: Part ownership. Sierra:Jazz: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria. Mayer:Novartis: Other: Travel support, Research Funding. Reinhardt:BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cerus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Medac: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; EUSA Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BlueBird Bio: Research Funding. Schulze-Rath:Bayer Pharma AG: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company. Hernández-Rivas:BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research Support, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research Support; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Lilly: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rovi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ossenkoppele:Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria; JAZZ: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie,: Consultancy, Honoraria; AGIOS: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; AMGEN: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Dohner:Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Berlin-Chemie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Brystol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Daiichi Sankyo Co, LTD: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead Sciences Inc: Consultancy, Honoraria; Agios: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Kronos Bio, Inc: Research Funding; Novartis AG: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer Inc: Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria; Syndax Pharmaceuticals Inc: Consultancy, Honoraria. Bullinger:Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Honoraria; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bayer Oncology: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal